Nov 3rd 2025
An Introduction to Parkinson’s Disease
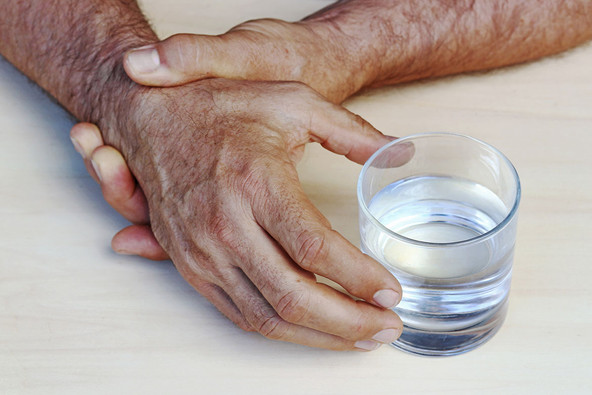
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is our most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s and one of the world’s fastest growing neurological disorders. About a million people had PD in 2017, costing the nation more than $51 billion. It is expected that more than 1.6 million will be living with PD by 2037.Although symptoms and symptom severity vary among individuals, PD generally starts with a tremor in the hands or arms. Other early symptoms include:1) Bradykinesia—slowness of movement in which the patient feels like they’re glued to the ground or chair and it’s hard to get going; this progressively erases body language and facial expression.2) Rigidity—stiffness and jerkiness in movement.3) Posture and balance problems—instability, stooped stance, impaired gait.However PD is a relentlessly progressive disease of neurological deterioration. In its most advanced stage PD is totally disabling. It makes your legs so “frozen” and stiff that it’s impossible to walk or even stand. At this st…
read more Fuel your life with the purest vitamins
Fuel your life with the purest vitamins